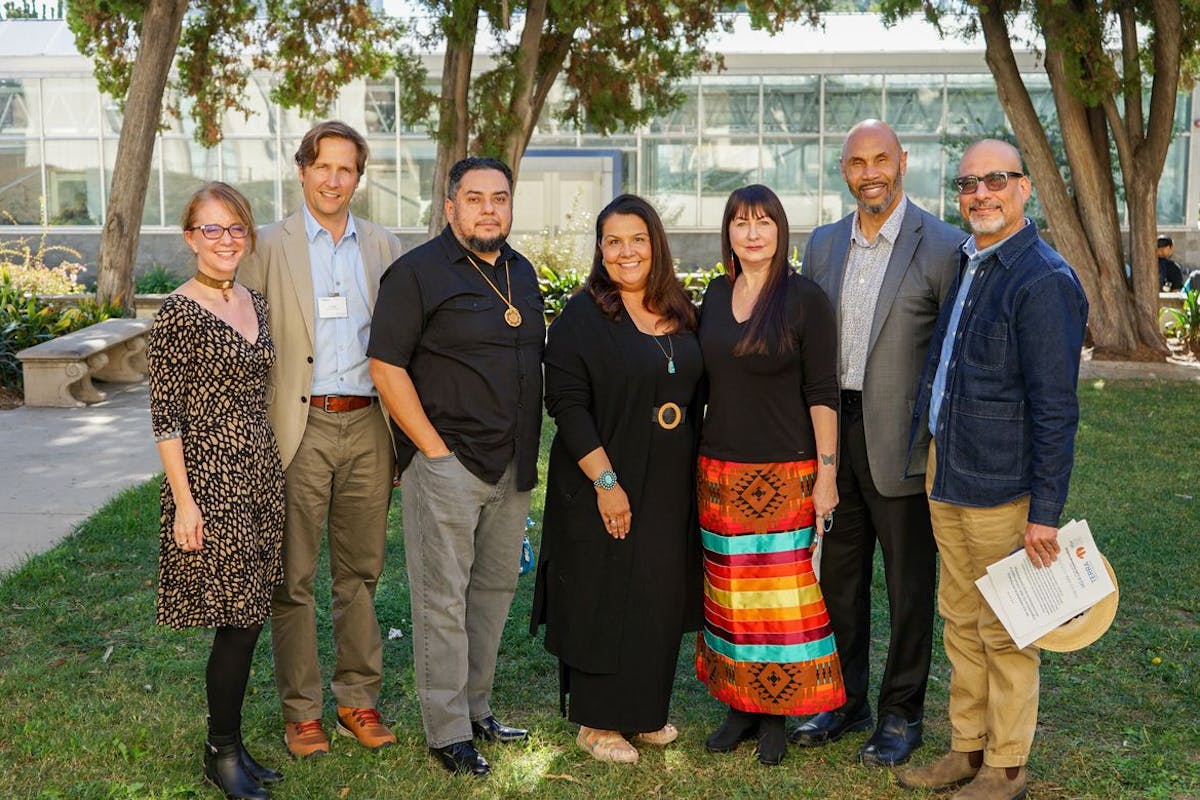
UCLA signs agreement with local tribal community for use of land

Key takeaways
- Members of the Gabrielino Tongva tribe will advise UCLA on planting and land caretaking practices across campus.
- A new basket weaving area, with 15 species of native plants, has opened in the Mildred E. Mathias Botanical Garden.
- Community members will help create programs for outdoor learning spaces such as Sage Hill, in the northwest corner of campus.
A new agreement between UCLA and members of the Gabrielino Tongva tribe will ensure that traditional ways of planting, harvesting and gathering are part of campus landscaping and caretaking practices.
The memorandum of understanding also establishes guidelines that provide access to the descendants of the original inhabitants of the land that UCLA has occupied for nearly 100 years for ceremonial events, workshops and community educational opportunities.
“It is with our deepest gratitude that we, the Gabrielino/Tongva San Gabriel Band of Mission Indians, enter into a partnership with UCLA,” said Anthony Morales, tribal chairman. “There are those that speak words and those that follow up with action. When action is taken, healing can begin. This is the first step of many that are needed to ensure our tribal members and ancestral home lands have a shared space where gathering can occur. We look forward to future endeavors and continued partnership with UCLA.”
In 2019 UCLA implemented an acknowledgement, now used during campus events and in official communications, that the campus is located on the traditional, ancestral lands of the Tongva. The new agreement is one of a series of recent developments at UCLA and across the University of California, that expand access to education for Native students.
In June, UCLA introduced the Native American and Pacific Islander Bruins Rising Initiative, which will create eight new faculty positions for scholars with expertise in American Indian and Pacific Islander Studies
And in April the University of California announced the Native American Opportunity Plan, ensure that in-state systemwide tuition and student service fees for California students from federally recognized Native American tribes are fully covered by grants or scholarships.
“We are in a time of welcome sea change for Native issues on campus with great support from the highest level of leadership,” said Shannon Speed, director of UCLA’s American Indian Studies Center and one of two special advisors on Native and Indigenous Affairs to UCLA Chancellor Gene Block. “I look forward to working with tribal leaders and the community to fully realize the potential of the agreement, as well as develop future endeavors of mutual benefit to the Tongva community and to UCLA.”
UCLA is one of a handful of colleges and universities across the country that are formalizing such agreements with tribal communities. The memorandum addresses several goals expressed during listening sessions with the community.
“We recognize that Native Americans are not only an important part of our history, but also an important part of our present and our future,” said Darnell Hunt, UCLA’s executive vice chancellor and provost. “And we’re very proud that UCLA has taken steps to ensure that our relationships to Native communities are centered on respect and service.”
The memorandum, which aligns with the goals of the campus’s sustainability plan, was developed and co-written by Mishuana Goeman, a former special advisor on Native and Indigenous Affairs to Block.
“It is not enough to plant Native gardens and call it decolonization,” said Goeman, who is currently on leave from UCLA at the University at Buffalo. “We must instead plant gardens, nurture them through our actions with First Peoples and learn from those actions as we move forward. It is not just the work of one person on campus, but the responsibility of all of us to engage and learn and be better guests on Tovaangar,” referring to the large expanse of Gabrielino Tongva land in Southern California that includes the area in which UCLA is located.
“My hope is that the Gabrielino Tongva will always have a place on campus to gather, harvest and caretake on their traditional territory — it enriches us all to be in such a relationship,” Goeman said.
The new agreement also includes provisions related to Sage Hill, three acres of undeveloped land in the northwest corner of campus.
“The partnership with UCLA and the San Gabriel Band of Mission Indians is not just a step for the First People of Los Angeles; it is an enrichment to our community,” said Kimberly Morales Johnson, the tribal secretary. “Our ancestors lived in community and with Mother Earth with relational reciprocity and respect. Today marks the community of our land, UCLA and the Gabrielino/Tongva coming together to ensure the landscape reflects our native plant relatives and a gathering space for future generations to come.”
During the spring, local members of the Gabrielino Tongva tribe designed and planted a basket weaving garden in UCLA’s Mildred E. Mathias Botanical Garden. The area is now home to 15 types of native plants used for basket weaving, and the species will be identified by signage bearing their common names, Latin names and, when possible, names drawn from the Tongva language.
“It has been such an honor and privilege to work with the community on this partnership,” said Mercedes Dorame, a member of the Gabrielino Tongva tribe who signed the agreement. “As a UCLA alumna, it means so much to have our community’s presence on the UCLA campus, recognizing its location on our homelands.”